- Visual Basic Sample Codes Ebook. Visual Basic Sample Codes E-Book is written by our tutor, Dr.Liew. It comprises 258 pages of captivating contents and 48 fascinating Sample Codes.Perfect source of reference for your VB projects. Check it out by clicking the book picture.
- Visual Basic Editor is a separate application that is a part of Excel and opens whenever you open an Excel workbook. By default, it’s hidden and to access it, you need to activate it. VB Editor is the place where you keep the VB code.
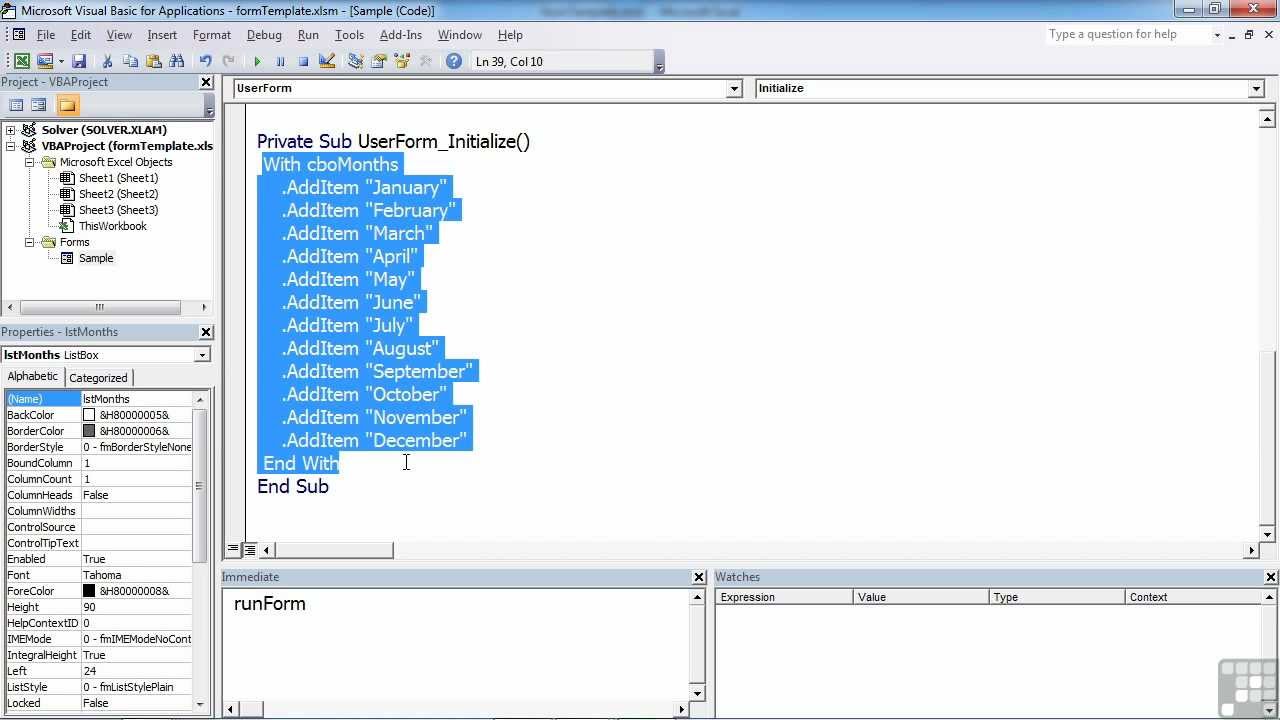
- Fundamentals of VBA Programming. This tutorial gives you a plenty of hands-on examples to get you started with excel macros. Let's understand a simple macro code. Let’s take a simple example multiplying a cell by 2. Sub Macro1 Range ('B2').FormulaR1C1 = '=RC -1.2'.
- Clicking the Visual Basic command on the Developer toolbar. Right-click on the name of the worksheet in the workbook (above the status bar) and the shortcut menu, choose the command 'View Code'. Another way to open the VB editor in Excel by pressing ALT+F11 key combination on the keyboard. How to copy the VBA macro code from some web site in.
Copy A Cell Range To The Clipboard. First, let's take a look at how you can copy all of the items.
VBA Conditional Statements
The main Excel VBA Conditional Statements are the If ... Then statement and the Select Case statement. Both of these evaluate one or more conditions and, depending on the result, execute specific sections of code.
The two Conditional Statement types are discussed individually below.
The Visual Basic If ... Then Statement
The If ... Then statement tests a condition and if it evaluates to True, executes a specific section of code. If the condition evaluates to False, a different section of code is executed.
The syntax of the If ... Then statement is:
| IfCondition1Then Code to be executed if Condition1 evaluates to True ElseIfCondition2ThenCode to be executed if Condition2 evaluates to True ElseCode to be executed if none of the previous conditions evaluate to True End If |
In the above If statement, you can add as many ElseIf conditions as you require. Alternatively, the ElseIf and the Else parts of the conditional statement can be omitted if desired.
In the example below, an If ... Then statement is used to color the current active cell, depending on the value of the cell contents.
| If ActiveCell.Value < 5 Then ActiveCell.Interior.Color = 65280 ' Color cell interior green ElseIf ActiveCell.Value < 10 ThenActiveCell.Interior.Color = 49407 ' Color cell interior orange ElseActiveCell.Interior.Color = 255 ' Color cell interior red End If |
Note that, in the above example, the If statement stops once it has satisfied a condition. Therefore, if the ActiveCell value is less than 5, the first condition is satisfied and so the cell is colored green. The If ... Then statement is then exited, without testing any further conditions.
For further information on the VBA If ... Then statement, see the Microsoft Developer Network website.
The Visual Basic Select Case Statement
The Select Case statement is similar to the If ... Then statement, in that it tests an expression, and executes different sections of code, depending on the value of the expression.
The syntax of the Select Case statement is:

| Select CaseExpression CaseValue1CaseValue2 End SelectActions if Expression matches Value2 Case ElseActions if expression does not match any of listed cases |
Visual Basic Code Examples In Excel Using
In the above code, the Case Else part of the conditional statement is optional.
In the following example, the Select Case statement is used to color the current active cell, depending on the value of the cell contents:
| Select Case ActiveCell.Value Case Is <= 5 End SelectActiveCell.Interior.Color = 65280 ' Color cell interior green Case 6, 7, 8, 9ActiveCell.Interior.Color = 49407 ' Color cell interior orange Case 10ActiveCell.Interior.Color = 65535 ' Color cell interior yellow Case ElseActiveCell.Interior.Color = 255 ' Color cell interior red |
The above example illustrates different ways of defining the different Cases in the Select Case statement. These are:
| Case Is <= 5 | This is an example of how you can test if your expression satisfies a condition such as <= 5 by using the keyword Case Is |
| Case 6, 7, 8, 9 | This is an example of how you can test if your expression evaluates to any one of several values, by separating the possible values by commas |
| Case 10 | This is an example of the basic test of whether your expression evaluates to a specific value |
| Case Else | This is an example of the 'Else' condition, which is executed if your expression hasn't matched any of the previous cases |
Visual Basic Code Examples In Excel For Beginners
Note that as soon as one case in the Select Case statement is matched, and the corresponding code executed, the whole Select Case statement is exited. Therefore, the code will never enter more than one of the listed cases.
Excel Visual Basic Programming Examples
For further information on the VBA Select Case statement, see the Microsoft Developer Network website.
Return to the Excel VBA Tutorial Page